Key Takeaways
- Tinnitus (ear ringing or cricket sounds) affects millions of Americans and can be managed through various relief strategies including sound masking and stress reduction
- Medical evaluation is essential to rule out underlying health conditions causing tinnitus, as removing earwax or treating infections can sometimes eliminate the symptom entirely
- Lifestyle modifications like reducing caffeine, alcohol, and salt intake can significantly decrease tinnitus intensity for many sufferers
- White noise machines, background music, and specialized sound therapy apps from Hearing Health Foundation can effectively mask the cricket sounds and provide relief
- Cognitive approaches like mindfulness meditation and tinnitus retraining therapy help patients make peace with their tinnitus rather than fighting against it
That constant cricket-like chirping in your ears isn’t just annoying—it’s affecting your quality of life. Whether you’ve been experiencing this sound for days or years, there are proven strategies to help reduce or even eliminate it.
Tinnitus—the medical term for hearing sounds with no external source—affects approximately 50 million Americans. The Hearing Health Foundation has developed numerous resources to help those suffering from these persistent sounds find relief through proper understanding and management techniques. Their specialized programs focus on both immediate relief and long-term coping strategies that have helped countless individuals regain their peace and quiet.
While many people describe tinnitus as ringing, others experience it as buzzing, hissing, whistling, or, as we’re focusing on today, cricket-like chirping. The good news is that you’re not alone, and there are effective ways to address this frustrating condition.
Why That Cricket Sound in Your Ears Won’t Go Away
“Tinnitus and Hearing Loss Treatment at …” from fortworthent.net and used with no modifications.
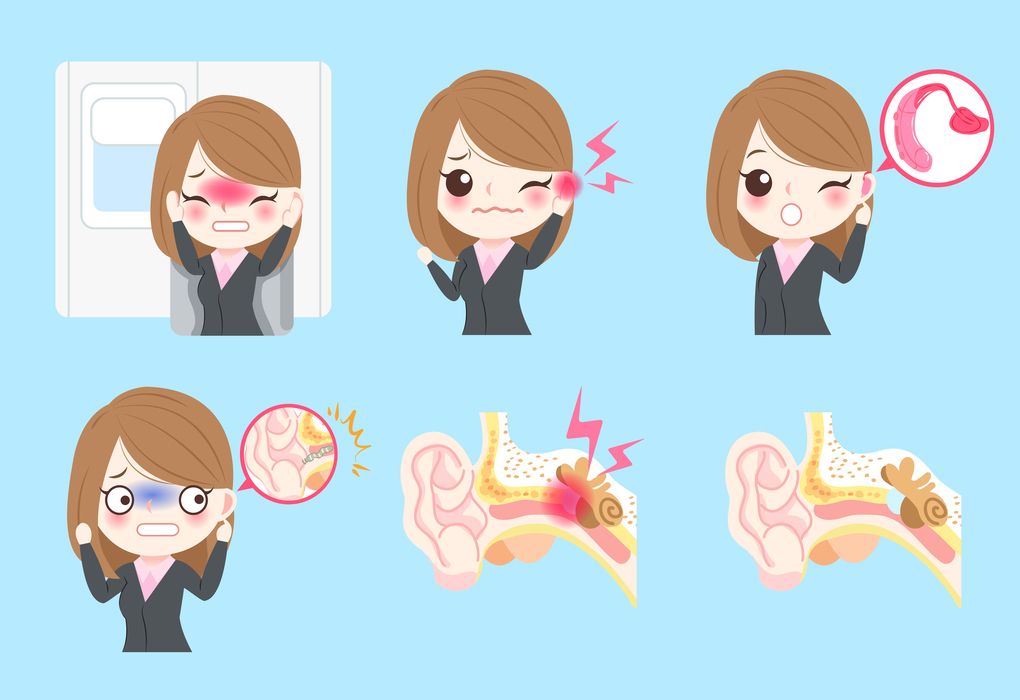
The persistent cricket sound you’re hearing isn’t actually produced by insects but by your auditory system. Tinnitus occurs when the normal sound-processing pathways in your brain are altered. This change forces your brain to adapt, sometimes resulting in the perception of phantom sounds like chirping or ringing.
For most people, tinnitus is subjective—meaning only you can hear it. It’s not a disease itself but rather a symptom that something has changed in your auditory system, including your ear, the auditory nerve that connects the inner ear to the brain, or the parts of the brain that process sound. For more information, you can explore common tinnitus questions answered by top audiologists.
The unpredictable nature of tinnitus can be particularly frustrating. Some days the cricket sounds might be barely noticeable, while other days they might seem overwhelming. This variability often correlates with stress levels, fatigue, and exposure to certain environmental factors.
What Causes the Cricket Sound in Your Ears
“Cricket Sound In-Ear Naturally …” from wavwatch.com and used with no modifications.
Understanding what triggers your tinnitus is the first step toward finding relief. While the exact mechanism behind tinnitus isn’t fully understood, several known factors can contribute to its development or worsening.
The Tinnitus-Cricket Connection
The “cricket” sound many patients describe is typically a high-pitched, rhythmic chirping sensation. This specific manifestation of tinnitus often relates to damage to the high-frequency hearing cells in the inner ear. These specialized cells, once damaged, can send incorrect signals to your brain that are interpreted as chirping or cricket-like sounds.
Interestingly, some patients don’t immediately recognize their tinnitus as an internal sound. As one Hearing Health Foundation case study reports, “Before Wendy could recognize that she was experiencing tinnitus, she thought that her garage was infested with crickets.” This confusion is common, as the brain struggles to make sense of these new phantom sounds.
Common Triggers That Worsen Cricket Sounds
While the underlying cause of tinnitus varies from person to person, certain factors consistently trigger or intensify symptoms. Identifying your personal triggers can dramatically improve your management strategy and quality of life. For more information on effective management, check out our guide on tinnitus management.
- Loud noise exposure (concerts, power tools, gunshots)
- Earwax buildup or blockage
- Certain medications (particularly some antibiotics, cancer drugs, and high doses of aspirin)
- Hearing loss due to aging or noise exposure
- Head or neck injuries
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders
- High stress levels and anxiety
- Alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco use
- High sodium diets
- Lack of sleep or poor sleep quality

Audiological Reasons Behind the Persistent Chirping
From an audiological perspective, tinnitus often stems from changes in the neural activity within your auditory pathways. When hair cells in the cochlea are damaged—whether from noise exposure, aging, or other factors—they can send random electrical impulses to your brain, which interprets these signals as sound.
This damage creates a form of “neural noise” in the auditory system. Your brain, attempting to compensate for this unusual activity, essentially turns up its own volume control, making you more aware of the phantom sounds. This explains why tinnitus often appears alongside hearing loss but can also occur in people with normal hearing.
When to See a Doctor About the Cricket Noise
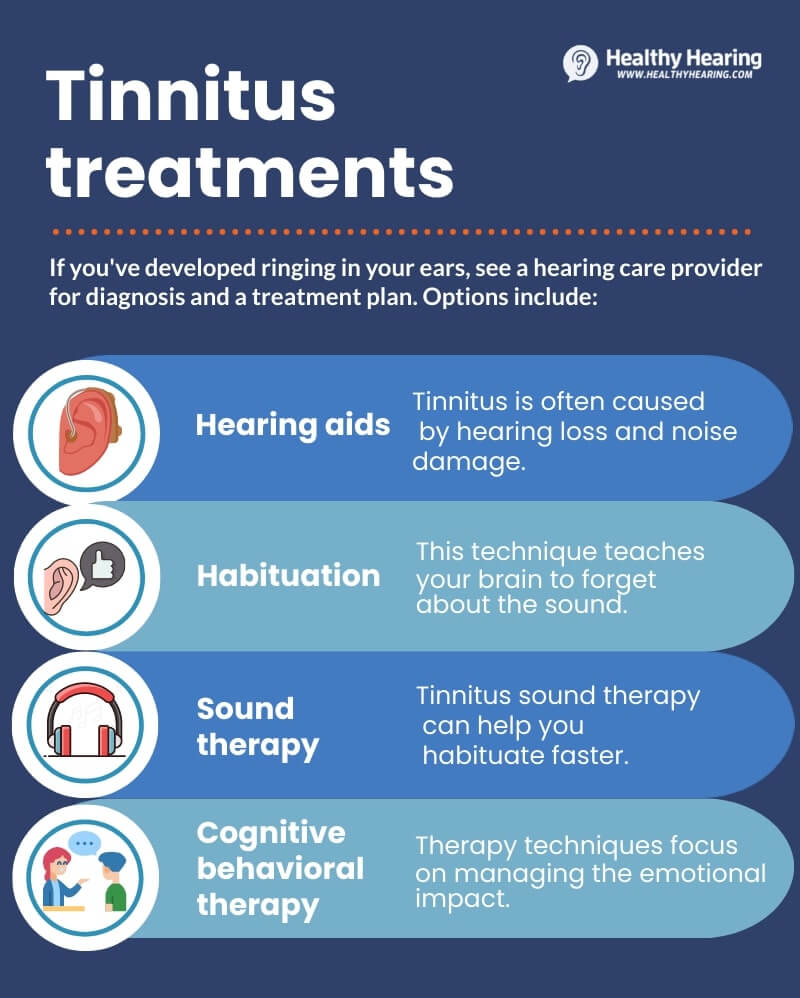
“Understanding and Managing Tinnitus: My …” from hearingaiddoctors.com and used with no modifications.
While some tinnitus cases may resolve on their own, persistent cricket sounds warrant medical attention. If you’ve experienced tinnitus for more than a week, or if it’s severe enough to affect your concentration, sleep, or quality of life, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
Certain tinnitus symptoms require immediate medical evaluation. If your cricket sounds began suddenly, are accompanied by dizziness or vertigo, or occur with hearing loss, contact your doctor right away. These could indicate a more serious underlying condition. Similarly, if your tinnitus is pulsatile (synchronized with your heartbeat) or appears alongside neurological symptoms like headaches or facial numbness, don’t wait to seek medical attention. For more information, you can read about tinnitus symptoms and their implications.
Tinnitus that develops after a head injury or ear trauma also requires prompt assessment. In about 10% of cases, tinnitus interferes with daily life so severely that professional intervention becomes necessary not just for the symptom itself, but for the anxiety and depression that can develop alongside it.
What to Expect During Your ENT Appointment
When you visit an ear, nose, and throat specialist (ENT or otolaryngologist) for tinnitus evaluation, they’ll likely begin with a comprehensive medical history. Be prepared to discuss when your symptoms started, their characteristics, and any factors that seem to worsen or improve them. The doctor will examine your ears with an otoscope to check for visible issues like earwax blockage or infection that could be causing the cricket sounds.
Your ENT may also assess your head, neck, and jaw movement to identify any structural problems contributing to your tinnitus. They’ll likely refer you for a hearing test conducted by an audiologist to determine if hearing loss is present, as this often accompanies tinnitus. Don’t be surprised if your doctor also orders additional tests like blood work to rule out conditions such as anemia or thyroid disorders that can contribute to tinnitus.
Diagnostic Tests That Help Identify Tinnitus Causes
A comprehensive tinnitus evaluation typically includes several specialized tests beyond the basic physical examination. Audiometric testing precisely measures your hearing sensitivity across different frequencies and can help determine if your tinnitus is related to hearing loss. Tympanometry evaluates your middle ear function and can identify issues like fluid buildup or eardrum problems. For more information on how to manage tinnitus effectively, explore tinnitus treatment options.
Some patients may undergo imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans to rule out structural abnormalities, especially if the tinnitus affects only one ear or is accompanied by other symptoms. Your doctor might also recommend specialized tests to characterize your tinnitus, including pitch matching (determining the frequency of your tinnitus) and loudness matching (measuring how loud your tinnitus sounds to you). These assessments help guide treatment approaches and monitor changes over time. For more information on effective treatment options, you can explore tinnitus treatment medications.
7 Immediate Relief Strategies for Cricket Sounds
“Amazon.com: The Tinnitus Solution: A …” from www.amazon.com and used with no modifications.
1. Sound Masking Techniques
Sound masking works by introducing external sounds that partially or completely cover up the cricket noise in your ears. This technique doesn’t eliminate tinnitus, but it makes it less noticeable by giving your brain something else to focus on. Effective masking sounds include white noise, pink noise, nature sounds like rainfall or ocean waves, and even low-level background music. The key is finding sounds that are more pleasant and less intrusive than your tinnitus. Many patients report that matching the pitch of the masking sound to their tinnitus frequency provides the most relief, though this may require some experimentation to find your perfect match.
2. Relaxation Exercises to Reduce Tinnitus Awareness
The relationship between stress and tinnitus creates a vicious cycle – stress worsens tinnitus, and tinnitus increases stress. Breaking this cycle through relaxation techniques can significantly reduce the perceived intensity of cricket sounds. Progressive muscle relaxation involves tensing and then releasing each muscle group in your body, creating a profound sense of physical relaxation that can diminish tinnitus awareness. Deep breathing exercises that focus on slow, diaphragmatic breathing activate your parasympathetic nervous system, counteracting the stress response that often amplifies tinnitus. Just 10-15 minutes of guided meditation daily can train your brain to detach from the emotional reaction to tinnitus, making the sound less bothersome even when present.
3. Avoiding Triggers That Make the Sound Worse
Once you’ve identified your personal tinnitus triggers through careful tracking, actively avoiding them can provide immediate relief. For many sufferers, limiting consumption of caffeine, alcohol, and high-sodium foods results in noticeable improvement within days. Environmental noise exposure is another common trigger – wearing earplugs or noise-canceling headphones in loud environments prevents both immediate tinnitus spikes and further hearing damage. Some medications can exacerbate tinnitus, so consult with your doctor about possible alternatives if you suspect a prescription is worsening your symptoms. For those whose tinnitus is aggravated by TMJ issues, avoiding excessive jaw movements like chewing gum and adopting proper jaw positioning can provide substantial relief.
4. White Noise Machines and Apps
White noise machines create a consistent sound across all audible frequencies, effectively masking the cricket sounds that characterize certain forms of tinnitus. These devices come in various forms, from dedicated bedside machines to small, portable units that can be carried throughout the day. Most modern options offer multiple sound profiles beyond pure white noise, including pink noise (which emphasizes lower frequencies) and brown noise (which has even more energy in the lower frequencies). Smartphone apps provide a convenient alternative, with many offering customizable soundscapes specifically designed for tinnitus relief. The most effective apps include features like sound mixing, timer functions, and the ability to create personalized sound profiles that precisely target your specific tinnitus frequency.
5. Background Music Therapy
Music therapy offers unique advantages over other sound masking techniques because it engages multiple brain regions simultaneously. This neurological engagement can help redirect attention away from tinnitus and provide emotional comfort. Classical music with its complex patterns and lack of lyrics is particularly effective for many tinnitus patients, though personal preference plays an important role in selection. Some audiologists recommend music with a tempo of 50-60 beats per minute, which corresponds to a relaxed heart rate and promotes calm.
Specialized notched music therapy, where frequencies matching your specific tinnitus are filtered out of the music, has shown promising results in clinical studies. This approach aims not just to mask but potentially to retrain the brain’s response to tinnitus over time. For best results, use high-quality headphones that provide clear sound without requiring excessive volume, as loud music can potentially worsen tinnitus in the long run.
Living With Chronic Cricket Sounds
“Tinnitus Symptoms: Common Sounds of Ear …” from www.healthyhearing.com and used with no modifications.
For many individuals, tinnitus becomes a long-term companion rather than a temporary visitor. Learning to coexist with the cricket sounds in your ears requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the physical sensation and your psychological response to it. The most successful long-term tinnitus managers don’t just treat the symptom—they transform their relationship with it through acceptance, adaptation, and consistent self-care practices. For more insights, you can read about making peace with tinnitus.
Building Your Tinnitus Support Network
The journey with chronic tinnitus doesn’t have to be a solitary one. Connecting with others who understand your experience can provide invaluable emotional support and practical advice. The American Tinnitus Association and Hearing Health Foundation offer online forums where you can share experiences with fellow tinnitus sufferers. Many communities also have in-person support groups where you can discuss coping strategies and feel less isolated in your experience. Don’t hesitate to involve family members and close friends in your tinnitus education—helping them understand what you’re experiencing makes it easier for them to provide the support you need. Remember that healthcare professionals including audiologists, ENT specialists, and mental health counselors should be core members of your support team, providing ongoing care as your condition and needs evolve.
Mental Health Strategies for Long-term Management
The psychological impact of persistent cricket sounds cannot be overstated. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has emerged as one of the most effective approaches for tinnitus management, helping patients identify and change negative thought patterns about their condition. Rather than focusing on eliminating the sound, CBT helps you modify your emotional and behavioral responses to it, significantly reducing tinnitus-related distress.
Mindfulness meditation teaches present-moment awareness without judgment, allowing you to observe your tinnitus without the automatic negative reactions that amplify distress. Regular practice can create distance between you and your tinnitus, reducing its emotional impact. As one patient from the Hearing Health Foundation shared, “Before I could recognize that I was experiencing tinnitus, I thought my garage was infested with crickets. Now I can acknowledge the sound without letting it control my emotions.” For more insights, explore how transcendental meditation alleviates symptoms of tinnitus.
Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT) combines sound therapy with educational counseling to help your brain reclassify tinnitus as a neutral rather than threatening signal. This neurological retraining can take 12-24 months but offers significant long-term relief for many patients. The goal isn’t silence but rather reaching a point where tinnitus no longer dominates your attention or triggers emotional distress.
Your Path Forward Without the Chirping
“Top treatments and remedies for ear ringing” from www.healthyhearing.com and used with no modifications.
While complete elimination of tinnitus isn’t always possible, substantial improvement is achievable for most sufferers. The combination of medical evaluation, sound therapy, lifestyle modifications, and psychological approaches creates a comprehensive management strategy that reduces both the perceived intensity of tinnitus and its impact on your quality of life. The most successful patients approach tinnitus management as an ongoing process rather than seeking a quick fix—consistency with your chosen interventions yields the greatest benefits over time.
Remember that tinnitus often fluctuates in intensity, with good days and challenging periods. These natural variations aren’t signs of failure but rather opportunities to practice your coping strategies. By tracking your progress over months rather than days, you’ll likely notice gradual improvement in your relationship with tinnitus. Many patients report that while the cricket sounds remain audible, they eventually fade into the background of awareness, much like the ticking of a clock that you stop noticing over time. The Hearing Health Foundation continues to fund promising research into new tinnitus treatments, offering hope for even better management options in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Living with tinnitus generates many questions about management, prognosis, and daily accommodations. Here are answers to the most common concerns expressed by those experiencing cricket sounds in their ears.
Can tinnitus (cricket sounds in ears) go away on its own?
Yes, tinnitus can sometimes resolve on its own, particularly when it’s caused by temporary factors like ear infections, medication side effects, or short-term noise exposure. Temporary tinnitus typically improves within days to weeks once the underlying cause is addressed. However, tinnitus lasting longer than three months is considered chronic and less likely to disappear completely without intervention. Even chronic tinnitus can become less noticeable over time through a combination of natural habituation (your brain learning to tune out the sound) and active management strategies. If your tinnitus is recent, eliminating potential triggers and protecting your hearing gives you the best chance for natural resolution.
Does wearing headphones make tinnitus worse?
Headphone use can impact tinnitus, but whether it worsens or helps depends entirely on how they’re used. Listening to audio at high volumes (above 85 decibels) can damage hearing and worsen existing tinnitus or create new cases. However, headphones used at moderate volumes can actually help manage tinnitus through sound therapy and masking techniques. Noise-canceling headphones are particularly beneficial for tinnitus sufferers, as they reduce the need to increase volume in noisy environments. If you use headphones, follow the 60/60 rule: listen at no more than 60% of maximum volume for no longer than 60 minutes at a time. Over-ear headphones generally create less pressure on the ear canal than in-ear models, making them preferable for many tinnitus patients.
What foods should I avoid if I have tinnitus?
Dietary triggers vary significantly between individuals, but several categories of food and drink frequently worsen tinnitus symptoms. Caffeine tops the list for many sufferers, with coffee, tea, energy drinks, and chocolate all potentially increasing tinnitus intensity by stimulating the nervous system and restricting blood vessels. Alcohol consumption, particularly red wine, can temporarily worsen tinnitus by altering blood flow to the inner ear. Foods high in sodium contribute to increased blood pressure, which can amplify tinnitus symptoms—processed foods, canned soups, and restaurant meals often contain hidden sodium. For more insights on managing tinnitus, check out this tinnitus treatment guide.
MSG (monosodium glutamate) is a common trigger that affects the neurotransmitters involved in hearing function. Some patients also report worsening symptoms with aspartame and other artificial sweeteners. The best approach is keeping a food diary alongside your tinnitus symptoms to identify your personal triggers, then testing elimination of suspect foods one at a time to confirm their impact. Many patients discover that while dietary modifications don’t eliminate their tinnitus, they can significantly reduce its intensity and frequency of flare-ups.
Is there a cure for the cricket sound in my ears?
Currently, there is no universal cure for tinnitus, but that doesn’t mean you’re without effective options. In cases where tinnitus has an identifiable cause like earwax blockage, medication side effects, or certain medical conditions, treating the underlying issue can eliminate the symptom. For instance, removing impacted earwax or treating an ear infection may completely resolve the cricket sounds. However, for the majority of chronic tinnitus cases related to sensorineural hearing loss or nerve damage, complete elimination isn’t currently possible. For more insights on treatments, you can explore what works and what doesn’t in tinnitus treatment.
This doesn’t mean you’re without hope—many management strategies can reduce tinnitus to the point where it no longer significantly impacts quality of life. Research into tinnitus treatments continues to advance, with promising developments in neuromodulation techniques, sound therapy protocols, and pharmaceutical interventions. The Hearing Health Foundation and other research organizations continue to fund studies aimed at developing more effective treatments and, ultimately, a cure for different types of tinnitus.
How do I sleep better with constant ringing or cricket sounds?
- Use a bedside sound machine that plays white noise, nature sounds, or other masking sounds throughout the night
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule to strengthen your body’s natural sleep cycle
- Create a cool, dark, comfortable sleep environment that minimizes other sensory distractions
- Practice a relaxing pre-sleep routine that might include gentle stretching, meditation, or a warm bath
- Avoid screens for at least an hour before bedtime, as blue light can disrupt sleep hormones
- Consider a specially designed tinnitus pillow with built-in speakers that deliver masking sounds directly to your ears
- Limit fluid intake in the evening to reduce nighttime bathroom trips that can disrupt sleep
Many tinnitus sufferers find that their symptoms seem worse at night when environmental sounds no longer provide natural masking. This heightened awareness can create anxiety about sleep, creating a cycle of insomnia and increased tinnitus distress. Breaking this cycle often requires addressing both the tinnitus directly and developing stronger sleep hygiene practices. Some patients benefit from short-term use of sleep aids prescribed by their doctor, though non-pharmaceutical approaches are generally preferred for long-term management.
If you struggle with sleep despite these strategies, consider consulting a sleep specialist. Sleep disorders like sleep apnea can worsen tinnitus, and addressing these underlying conditions often improves both sleep quality and tinnitus symptoms. Remember that improving sleep with tinnitus often requires consistency and patience—the benefits of better sleep habits typically accumulate over weeks rather than appearing immediately.
The journey to managing cricket sounds in your ears may have its challenges, but with the right approach, most people find significant relief. By combining medical evaluation, sound therapy, lifestyle modifications, and psychological techniques, you can develop a personalized strategy that works for your specific situation. Remember that tinnitus management is not about achieving perfect silence but rather reaching a point where the cricket sounds no longer dominate your awareness or limit your enjoyment of life.
The Hearing Health Foundation continues to support those affected by tinnitus through education, research funding, and community building. Their resources can help you stay informed about the latest developments in tinnitus management and connect with others sharing similar experiences. Whether you’re just beginning your tinnitus journey or have been managing it for years, remember that improvements are possible and you don’t have to face this challenge alone.