Key Takeaways
- OTC tinnitus treatments vary in effectiveness, with sound therapy devices showing the most consistent results compared to supplements and medications.
- Despite widespread marketing claims, no dietary supplement has received FDA approval specifically for treating tinnitus symptoms.
- Common supplements like Ginkgo biloba, zinc, and vitamin B12 have limited scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness for most tinnitus sufferers.
- Proper diagnosis of underlying causes is essential before starting any OTC tinnitus treatment regimen.
- Sound masking technologies provide immediate relief for many while addressing potential earwax impaction can resolve tinnitus in specific cases.
That persistent ringing, buzzing, or whooshing sound that no one else can hear is driving you crazy. You’re not alone – tinnitus affects millions of people worldwide who are desperately seeking relief without prescription medications. While no over-the-counter solution can completely cure tinnitus, several options might help manage those frustrating phantom sounds.
Finding effective tinnitus relief often requires a personalized approach, as what works for one person may not work for another. The Natural Ear Health Institute recommends trying several approaches systematically while tracking your results, as the underlying causes of tinnitus can vary dramatically between individuals. Understanding your options is the first step toward finding what might work for your specific situation.
Before diving into treatment options, it’s important to understand that tinnitus isn’t a disease itself but a symptom that can stem from numerous conditions. From noise-induced hearing damage to ear infections, medication side effects, or even stress – identifying the root cause can lead to more targeted and effective treatment approaches.
Article-at-a-Glance
Tinnitus can feel isolating, but approximately 15% of Americans (over 50 million people) experience some form of it. This guide explores the most accessible over-the-counter options that may provide relief, including sound therapy devices, dietary supplements, earwax removal products, and anti-inflammatory approaches. We’ll examine the science behind each option and provide practical guidance on what might work best for different types of tinnitus.
“Despite the prevalence of supplements marketed for tinnitus relief, the American Academy of Otolaryngology’s Clinical Practice Guidelines clearly state that dietary supplements are generally ineffective for reducing the perception of tinnitus for most patients. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.”
Many tinnitus sufferers turn to over-the-counter solutions when medical interventions prove costly, inconvenient, or ineffective. The appeal is understandable – these options are typically more affordable, readily available, and don’t require doctor visits. However, this self-treatment approach comes with important considerations about efficacy and safety.
The 7 Most Effective OTC Tinnitus Relief Options
“I Ranked Every Tinnitus Treatment – YouTube” from www.youtube.com and used with no modifications.
When it comes to managing tinnitus symptoms without a prescription, certain approaches have gained more credibility than others. Based on user reports and limited clinical evidence, the most promising options include sound masking devices, earwax removal systems (when appropriate), and specific supplements for those with corresponding deficiencies. Though not all of these work for everyone, they represent the current landscape of accessible tinnitus management tools that don’t require a doctor’s prescription.
What Causes Those Ringing Ears?
Tinnitus often begins after exposure to loud noise, which damages the delicate hair cells in your inner ear that transmit sound signals to your brain. When these cells are damaged, they can send random electrical impulses to your brain, which interprets them as sound. Age-related hearing loss, earwax buildup, certain medications (including aspirin, antibiotics, and some cancer drugs), head or neck injuries, and blood vessel disorders can all trigger or worsen tinnitus.
Stress and anxiety deserve special mention as they create a frustrating cycle with tinnitus – they can make tinnitus worse, while tinnitus itself often increases stress levels. This is why comprehensive tinnitus management often addresses both physical and psychological components. Understanding your specific triggers can help you choose the most appropriate over-the-counter treatment options.
Why People Turn to OTC Solutions
Prescription treatments for tinnitus can be expensive, especially for those without comprehensive insurance coverage. Many patients report frustration after medical consultations that end with the disheartening “learn to live with it” advice. This leaves sufferers searching for accessible alternatives they can try independently.
Over-the-counter options provide a sense of control over a condition that can feel overwhelming. They offer immediate action steps when medical interventions seem limited. Many tinnitus patients appreciate being able to try different approaches without multiple appointments, especially since tinnitus often requires personalized treatment strategies that may involve trial and error.
The convenience factor cannot be overlooked either. Being able to purchase potential solutions online or at local pharmacies makes these options particularly attractive to those who may have mobility issues, live in rural areas with limited specialist access, or simply prefer to manage their symptoms privately.
Medical vs. Self-Treatment Approaches
While the appeal of self-treatment is understandable, it’s crucial to distinguish when medical evaluation is necessary. Sudden-onset tinnitus, tinnitus in only one ear, tinnitus accompanied by dizziness, or tinnitus that pulsates with your heartbeat all warrant prompt medical attention. These symptoms could indicate underlying conditions that require professional intervention.
The safest approach combines medical guidance with complementary self-care. Start with a proper diagnosis from an audiologist or ENT specialist to rule out serious causes, then discuss which OTC options might complement your treatment plan. This balanced approach ensures you don’t miss underlying conditions while still exploring accessible relief options.
Sound Therapy Devices: The First Line of OTC Defense
“The 5 BEST Sound Machines for Tinnitus …” from www.youtube.com and used with no modifications.
Sound therapy represents one of the most evidence-backed approaches to tinnitus management available without prescription. These devices work by introducing external sounds that can distract your brain from the internal tinnitus sounds. The concept is simple yet effective: by providing alternative auditory stimulation, you reduce awareness of the unwanted sounds generated by your auditory system.
Unlike many supplements, sound therapy devices provide immediate relief for many users and pose minimal risk when used as directed. They’re particularly effective for nighttime use, when the silence can make tinnitus sounds seem louder and more intrusive. Many users report significant improvements in sleep quality and reduced tinnitus distress after incorporating sound therapy into their nightly routine.
White Noise Machines Worth Your Money
White noise machines have become a go-to solution for many tinnitus sufferers seeking immediate relief. These devices produce consistent background noise that helps mask the internal sounds of tinnitus. Unlike medication approaches that may take weeks to show effects, sound masking can provide immediate relief for many users during active use.
When selecting a white noise machine, look for devices with multiple sound options including white, pink, and brown noise variations, as different tinnitus frequencies respond better to different sound profiles. The LectroFan Classic and Marpac Dohm Classic consistently receive high ratings from tinnitus sufferers for their sound quality and reliability. Models with timers, portable options, and rechargeable batteries offer additional convenience for round-the-clock relief.
The most effective machines provide a balance of sound quality, volume control, and customization. Many users report that models with at least 10-20 different sound options increase the likelihood of finding effective relief, as tinnitus manifestations vary widely between individuals. For best results, position the device near your bed or primary relaxation area rather than across the room.
Sound Pillows for Nighttime Relief
Sound pillows represent an innovative solution specifically designed to address nighttime tinnitus disturbances. These specialized pillows contain built-in speakers that deliver soothing sounds directly to your ears without disturbing sleeping partners. The proximity of sound delivery often allows for lower volume levels while still effectively masking tinnitus.
The best sound pillows combine comfort with quality sound production and durable construction. Look for models with memory foam comfort layers, washable covers, and Bluetooth connectivity that allows you to stream your preferred sounds. Many users find that sound pillows provide the dual benefit of masking tinnitus while also improving overall sleep quality through gentle sound therapy.
Phone Apps That Actually Help
The digital revolution has brought tinnitus relief to our smartphones through specialized apps designed to generate masking sounds and even provide comprehensive tinnitus management programs. Leading apps like Resound Relief, Tinnitus Calmer, and MyNoise offer customizable soundscapes that can be tailored to match and mask your specific tinnitus frequency profile.
The most effective tinnitus apps go beyond basic sound generation to include features like frequency matching tools, hearing tests, and tinnitus tracking journals. This comprehensive approach allows users to identify patterns in their tinnitus triggers and relief methods. For optimal results, use these apps with quality headphones rather than phone speakers, particularly when precision frequency matching is needed to target your specific tinnitus profile.
Remember that while these apps can provide significant relief, using headphones for extended periods may not be practical or comfortable. Consider pairing app usage with external speakers during home relaxation and reserving headphone use for situations where external sounds can’t be controlled.
Portable Sound Generators to Try
For those who need tinnitus relief beyond the bedroom, portable sound generators offer on-the-go management options. These compact devices resemble hearing aids or earbuds but focus solely on producing masking sounds rather than amplifying external noise. They’re particularly valuable during quiet activities like reading, meditating, or working in silent environments where tinnitus often becomes more noticeable.
“The most effective tinnitus management approach often combines multiple strategies rather than relying on a single solution. A sound machine at night, portable maskers during quiet daytime activities, and addressing nutritional deficiencies can create a comprehensive relief system tailored to your lifestyle and specific tinnitus pattern.”
When evaluating portable generators, battery life becomes a critical feature, with the best options offering at least 10-15 hours of continuous use. Models with rechargeable batteries provide better long-term value compared to those requiring frequent battery replacement. While premium medical-grade devices offer the most customization, several consumer models provide effective relief at more accessible price points. For more information on tinnitus treatment options, you can visit this comprehensive guide.
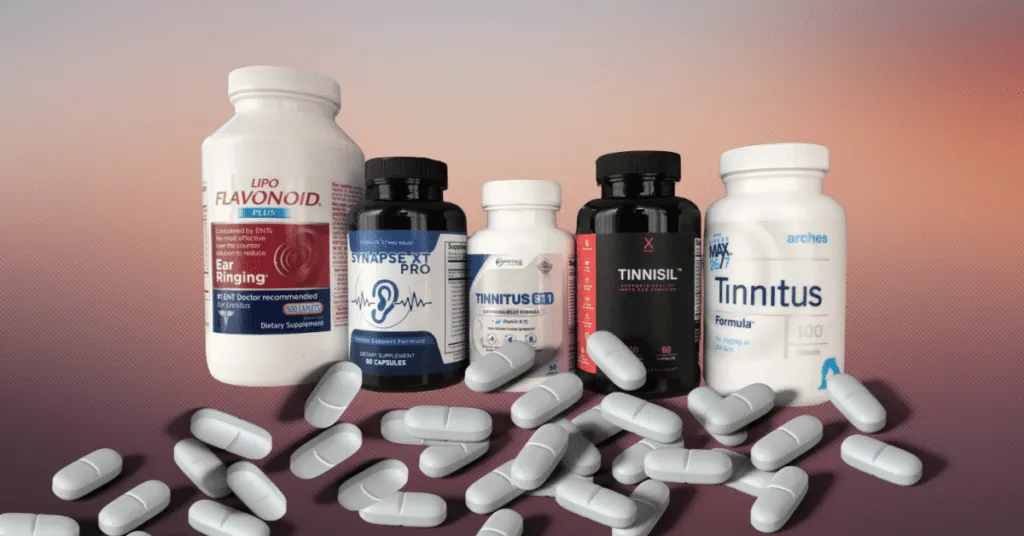
Herbal Supplements That Target Tinnitus
“5 Most Popular Supplements For Tinnitus” from treblehealth.com and used with no modifications.
Herbal supplements represent one of the most widely marketed yet controversial approaches to tinnitus management. Despite their widespread availability and compelling marketing claims, the scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness varies significantly. Understanding the research behind these options helps set realistic expectations about their potential benefits.
Most herbal supplements work on the premise of improving blood circulation to the ear, reducing inflammation, or providing neuroprotective effects for auditory structures. The challenge lies in the varying quality of ingredients, inconsistent manufacturing standards, and individual differences in how people respond to botanical interventions. Patience is essential when trying herbal approaches, as benefits typically require consistent use over several weeks or months. For those interested in exploring these options further, here is a comprehensive guide on natural treatment for tinnitus that discusses effective approaches backed by research.
- Start with single-ingredient supplements to better identify what works
- Look for standardized extracts with specified active compound percentages
- Choose products that follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
- Be wary of proprietary blends that don’t disclose exact amounts of ingredients
- Keep a daily journal to track changes in tinnitus symptoms during supplementation
Always consult with a healthcare provider before beginning any supplement regimen, especially if you take prescription medications or have underlying health conditions. Some herbal ingredients can interact with blood thinners, blood pressure medications, and other common prescriptions.
Ginkgo Biloba: Science and Real Results
Ginkgo biloba stands as perhaps the most researched herbal supplement for tinnitus, with studies dating back decades. Its proposed mechanism centers on improving microcirculation to the inner ear and providing neuroprotective effects through its flavonoid and terpenoid components. Scientific research shows mixed results, with some studies demonstrating modest benefits while others show little to no improvement compared to placebo.
| Study | Participants | Duration | Dosage | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Holgers et al. (1994) | 80 patients | 12 weeks | 150mg daily | Modest improvement in 35% of subjects |
| Drew & Davies (2001) | 1121 patients | 12 weeks | 120-240mg daily | No significant difference vs. placebo |
| von Boetticher (2011) | 94 patients | 8 weeks | 240mg daily | Significant improvement in tinnitus severity |
For those considering ginkgo, quality matters tremendously. Look for standardized extracts containing 24% flavone glycosides and 6% terpene lactones, which reflect the concentrations used in most clinical studies. The typical recommended dosage ranges from 120-240mg daily, divided into 2-3 doses. Improvement, when it occurs, typically begins after 4-6 weeks of consistent use.
It’s worth noting that ginkgo has blood-thinning properties and shouldn’t be combined with anticoagulant medications or taken before surgery. Side effects are generally mild but can include headache, digestive upset, and allergic reactions. The inconsistent research results suggest ginkgo may help some individuals while providing little benefit to others, potentially depending on the underlying cause of tinnitus.
Many audiologists suggest a 12-week trial period with ginkgo is reasonable for patients without contraindications, after which benefits should be evaluated before deciding whether to continue long-term use. Document your tinnitus levels before starting supplementation to provide a clear baseline for comparison.
Lipo-Flavonoid: Does This Popular Option Work?
Lipo-Flavonoid stands as one of the most heavily marketed OTC tinnitus supplements, featuring a proprietary blend centered around lemon bioflavonoids alongside B vitamins and other nutrients. The formula is based on research from the 1960s suggesting that bioflavonoids might improve inner ear circulation. Despite decades on the market and numerous testimonials, independent clinical studies validating its effectiveness specifically for tinnitus remain surprisingly limited. For more insights, check out this article on tinnitus treatment options.
The supplement’s primary ingredient, eriodictyol glycoside (a lemon bioflavonoid), theoretically works by improving microcirculation in the inner ear and providing antioxidant protection to delicate ear structures. Secondary ingredients like vitamins B6, B12, and C may address potential nutritional deficiencies that could contribute to tinnitus symptoms. Most users who report benefits notice gradual improvements rather than immediate relief, typically after 3-4 weeks of consistent use at the recommended dosage of two capsules three times daily with meals.
Ring Stop and Other Multi-Ingredient Formulas
Ring Stop represents another popular multi-ingredient tinnitus formula containing a proprietary blend of herbs like garlic, ginkgo biloba, and zinc. These combination products appeal to consumers seeking comprehensive support through multiple mechanisms of action. The synergistic approach aims to address various potential causes simultaneously, from circulation issues to inflammation and oxidative stress.
Unlike single-ingredient supplements, these formulations make evaluation of effectiveness more challenging, as it’s difficult to determine which component might be providing benefit (if any). This complexity also increases the potential for ingredient interactions and side effects. The most reputable multi-ingredient formulas provide transparency about exact amounts of each ingredient rather than hiding behind proprietary blend labels that only list total amounts.
Consumer reviews for these products tend to show polarized results – some users report significant improvements while others experience no benefit whatsoever. This inconsistency likely reflects the heterogeneous nature of tinnitus itself, with different underlying causes responding differently to various ingredients. For best results, choose formulas manufactured by companies that can provide evidence of quality testing and standardization of key botanical ingredients.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals for Ear Health
“Find the Best Find the Best Supplements …” from stanfordhearingaids.com and used with no modifications.
Certain nutritional deficiencies may contribute to tinnitus symptoms or exacerbate existing tinnitus. The connection between nutrition and ear health centers primarily around nerve function, inflammation regulation, and cellular protection within auditory structures. While supplements won’t cure most forms of tinnitus, addressing specific deficiencies may help reduce symptom severity in certain individuals.
The most promising micronutrients for tinnitus management include those involved in nerve signaling, antioxidant protection, and cellular energy production. Rather than supplementing blindly, consider asking your healthcare provider for appropriate blood tests to identify specific deficiencies that might be contributing to your symptoms. This targeted approach is more likely to yield benefits than random supplementation. For those interested in exploring alternative methods, there are natural treatments for tinnitus that are backed by research.
B12 Deficiency Connection to Tinnitus
Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in nerve health and function throughout the body, including the auditory system. Deficiency in this essential nutrient can contribute to demyelination (breakdown of the protective sheath around nerves), potentially affecting how sound signals are transmitted and processed. Multiple studies have identified connections between B12 deficiency and tinnitus, particularly in older adults and those following restricted diets.
Supplementation with B12 appears most beneficial for individuals with confirmed deficiencies rather than as a general tinnitus treatment. Testing is relatively inexpensive and can prevent unnecessary supplementation while identifying those most likely to benefit. The recommended forms for supplementation include methylcobalamin or adenosylcobalamin, which are typically better absorbed than the more common cyanocobalamin found in many multivitamins.
Those at highest risk for B12 deficiency include vegans, vegetarians, adults over 50, individuals with digestive disorders affecting absorption, and those taking certain medications including proton pump inhibitors and metformin. For these groups, B12 supplementation might provide meaningful improvements in tinnitus symptoms alongside other neurological benefits. Typical therapeutic dosages range from 1,000-5,000 mcg daily, with higher doses often used initially to correct deficiencies.
Zinc Supplements: Who Benefits Most
Zinc plays multiple roles in auditory function, serving as a component of the enzyme superoxide dismutase (an important antioxidant) and helping regulate cell growth and immune function within the ear. Research on zinc for tinnitus shows varying results, with the strongest benefits observed in individuals who have zinc deficiency and tinnitus with no other identifiable cause.
One notable study found that approximately 31% of tinnitus patients had zinc deficiency compared to 2% in the control group, suggesting a potential connection. Those with pre-existing deficiencies who supplemented with 50mg of zinc daily for two months showed significant improvement compared to those with normal zinc levels. This indicates that zinc supplementation may be most appropriate for the subset of tinnitus sufferers with documented deficiencies rather than as a universal treatment.
Common risk factors for zinc deficiency include vegetarian diets, excessive alcohol consumption, certain digestive disorders, and older age. Side effects of zinc supplementation can include nausea and altered taste, particularly at higher doses. Long-term high-dose supplementation should be avoided as it can interfere with copper absorption and immune function.
Magnesium for Noise-Induced Tinnitus
Magnesium shows particular promise for noise-induced tinnitus based on its role in protecting against cellular damage from excessive noise exposure. This essential mineral helps regulate glutamate activity (an excitatory neurotransmitter that can damage nerve cells when overactive) and improves blood flow to sensitive auditory structures. Some research suggests magnesium supplementation may provide both preventive and therapeutic benefits for noise-related hearing issues.
Military studies have shown that magnesium supplementation before noise exposure can reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss and associated tinnitus. For existing tinnitus, magnesium may be most beneficial for those with deficiencies or with symptoms that worsen after noise exposure. Common formulations include magnesium citrate, glycinate, and threonate, with the latter showing improved ability to cross the blood-brain barrier.
Typical dosages range from 200-400mg elemental magnesium daily, preferably divided into multiple doses to improve absorption and reduce digestive side effects. As with other nutrients, testing for deficiency can help identify those most likely to benefit from supplementation. Common signs of magnesium deficiency include muscle cramps, anxiety, insomnia, and headaches – symptoms that often co-occur with tinnitus.
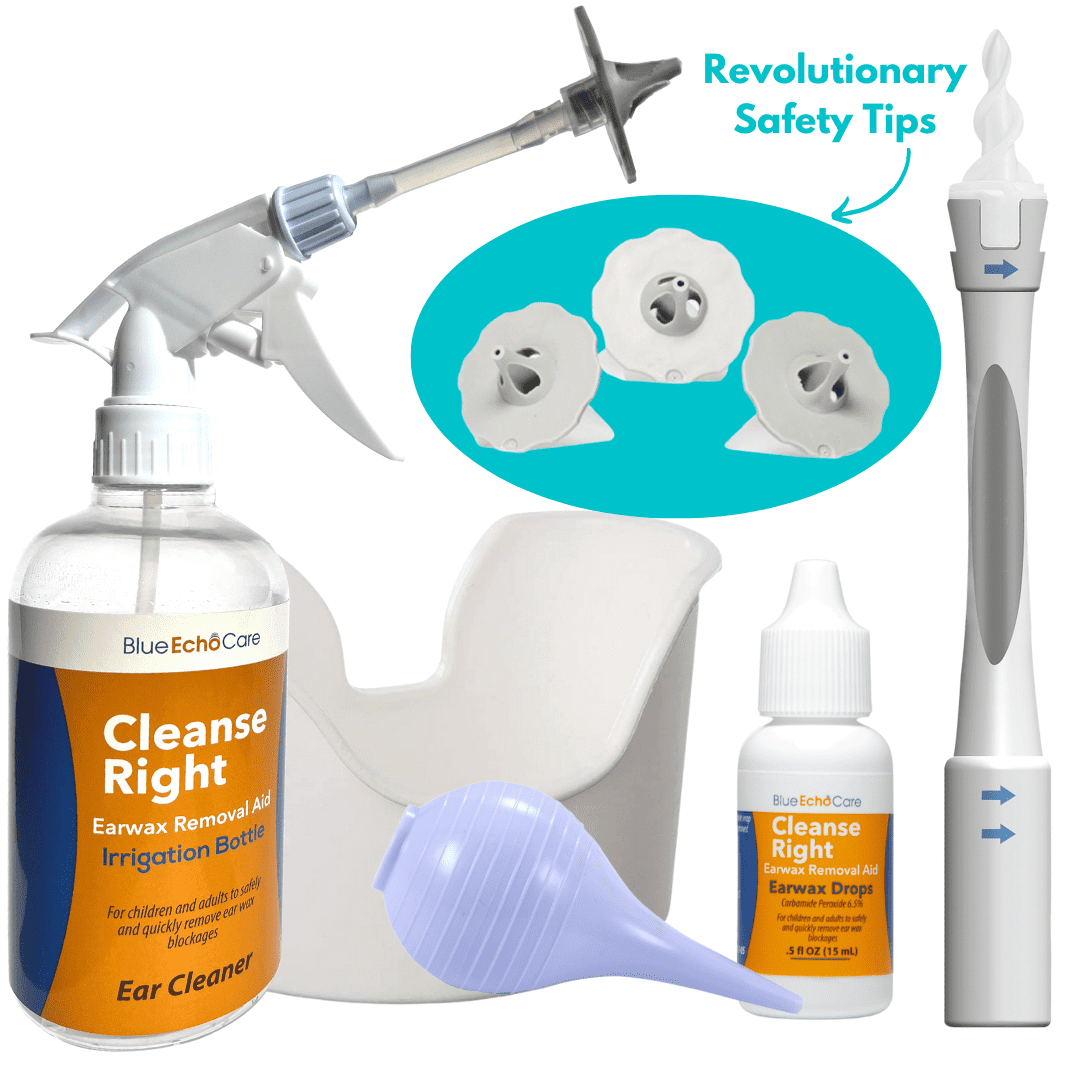
Earwax Removal Products: When They Help and Harm
“Ear Wax Removal Kit- FDA Approved …” from www.walmart.com and used with no modifications.
Excessive earwax (cerumen) can cause or exacerbate tinnitus by creating a blockage that alters how sound travels through the ear canal. This impaction can create pressure changes in the ear and temporarily affect hearing, often resulting in a ringing or buzzing sensation. OTC earwax removal products can provide significant relief in these specific cases, often resolving tinnitus symptoms completely once the blockage is cleared.
The most effective OTC options include irrigation kits with bulb syringes and earwax softening drops containing carbamide peroxide, glycerin, or mineral oil. These products work by softening hardened wax, making it easier to flush out gently. For best results, follow package instructions carefully, typically applying drops for 1-2 days before gentle irrigation. Avoid using cotton swabs, which can push wax deeper into the ear canal and worsen impaction.
It’s crucial to note that these products should only be used when excess earwax is the suspected cause of tinnitus. They should be avoided if you have a perforated eardrum, ear infection, ear tubes, or a history of ear surgery. If tinnitus persists after gentle wax removal attempts, consult a healthcare provider for professional evaluation and removal if necessary.
When Impacted Earwax Causes Tinnitus
Identifying earwax-related tinnitus helps determine if earwax removal products might provide relief. Common signs include tinnitus that developed suddenly rather than gradually, a feeling of fullness or pressure in the affected ear, and tinnitus that changes in intensity when yawning or moving the jaw. Often, you might also notice reduced hearing in the affected ear, which can worsen when water enters the ear canal during bathing or swimming.
If you can see visible earwax buildup or if your healthcare provider has previously mentioned you produce excess earwax, OTC removal products may be particularly beneficial. Those who use hearing aids, earbuds, or earplugs regularly are at higher risk for wax impaction due to these devices potentially pushing wax deeper into the ear canal. Similarly, individuals who regularly use cotton swabs to clean their ears often inadvertently create impactions over time.
For safe home treatment, choose products specifically formulated for earwax removal rather than improvised solutions. Ear candling, despite its popularity in some alternative health circles, has not been proven effective and carries risks of burns, wax dripping into the ear canal, and eardrum perforation. When in doubt about the safety of home removal, particularly for severe or recurrent impactions, professional removal by a healthcare provider offers the safest approach.
OTC Anti-Inflammatory Options
“Lipo-Flavanoid Plus Tinnitus Supplement …” from www.walmart.com and used with no modifications.
Inflammation within the auditory system may contribute to tinnitus in various ways, from direct irritation of neural pathways to altered blood flow in tiny vessels serving the inner ear. While prescription anti-inflammatories are sometimes used for acute tinnitus, several over-the-counter options may provide modest benefits for inflammation-related tinnitus symptoms while carrying fewer risks of side effects with long-term use. For those seeking alternatives, there are natural treatment options for tinnitus that are backed by research.
The connection between inflammation and tinnitus appears strongest in cases resulting from acoustic trauma, infections, or autoimmune responses affecting the ear. For these specific causes, reducing inflammation may help decrease both the perceived intensity of tinnitus sounds and associated discomfort. However, results typically vary considerably between individuals, reflecting the complex and multifaceted nature of tinnitus mechanisms.
How Inflammation Affects Tinnitus
Inflammation can trigger or worsen tinnitus through several mechanisms. When inflammatory processes affect the cochlea or auditory nerve, they can alter how electrical signals are generated and transmitted to the brain. This disruption can create phantom sound perceptions experienced as tinnitus. Additionally, inflammation often increases blood flow to affected areas, which can create pressure changes and fluid accumulations that further impact auditory function.
Neuroinflammation (inflammation affecting neural tissues) appears particularly relevant to tinnitus persistence. Research suggests that inflammatory processes can sensitize neural pathways, making the brain more likely to generate and maintain tinnitus signals even after the initial trigger has resolved. This mechanism may explain why some cases of temporary tinnitus become chronic despite no ongoing physical damage to the ear structures. For more insights on this topic, consider exploring tinnitus treatment medications and their effects.
The relationship between systemic inflammation and tinnitus suggests that addressing inflammation broadly, rather than just locally in the ear, might provide benefits for some sufferers. This connection helps explain why some individuals report tinnitus improvements when following anti-inflammatory diets or addressing inflammatory conditions elsewhere in the body.
Non-Prescription Options That Reduce Ear Inflammation
Several OTC approaches show promise for addressing inflammation-related tinnitus. Traditional NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen can provide temporary relief during acute tinnitus flares but aren’t recommended for long-term use due to potential side effects including digestive issues and increased bleeding risk. For those seeking gentler options for ongoing management, natural compounds with anti-inflammatory properties offer alternatives with generally favorable safety profiles.
Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil or algae sources demonstrate systemic anti-inflammatory effects that may benefit vascular and neural aspects of tinnitus. Typical therapeutic dosages range from 1,000-3,000mg combined EPA/DHA daily, preferably from pharmaceutical-grade sources tested for contaminants. Similarly, curcumin (from turmeric) shows promising anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, though its poor absorption necessitates choosing formulations with enhanced bioavailability through technologies like liposomal delivery or piperine addition.
Topical approaches include OTC ear drops containing calendula or other botanical anti-inflammatories, which may provide localized relief for outer and middle ear inflammation. These should only be used when the eardrum is intact and no infection is present. For inflammation triggered by allergies, non-drowsy antihistamines like cetirizine or loratadine may reduce associated tinnitus symptoms during allergy seasons.
Choosing the Right OTC Treatment for Your Tinnitus Type
“Lipo-Flavonoid Plus Day/Night Tinnitus …” from www.walmart.com and used with no modifications.
The effectiveness of any tinnitus treatment largely depends on matching the approach to your specific type and cause of tinnitus. With dozens of OTC options available, strategic selection based on symptom patterns and likely causes offers the best path to finding relief. This personalized approach requires honest assessment of your symptoms, potential triggers, and how your tinnitus responds to different interventions.
Begin by categorizing your tinnitus: Is it constant or intermittent? Does it worsen with certain activities or environments? Is it accompanied by hearing loss, dizziness, or fullness sensations? These characteristics can provide important clues about underlying mechanisms and guide more targeted treatment selection. Remember that combined approaches often yield better results than single interventions, particularly for chronic or severe tinnitus.
The Truth About Treatment Effectiveness
When evaluating tinnitus treatments, maintaining realistic expectations is crucial for avoiding frustration and wasted resources. No current OTC option provides complete tinnitus elimination for most chronic sufferers. Instead, successful management typically involves reducing symptom intensity, decreasing awareness, and minimizing impact on daily functioning rather than achieving silence.
The most evidence-supported OTC approach remains sound therapy, which consistently demonstrates effectiveness for masking tinnitus and reducing its perceived intensity during use. Supplemental approaches show much more variable results, with benefits often limited to specific subgroups with relevant deficiencies or underlying conditions. This reality explains why identical treatments produce dramatically different outcomes between individuals.
Marketing claims for tinnitus products frequently overstate potential benefits and minimize limitations. When evaluating product claims, look for specific references to peer-reviewed research rather than vague testimonials. Be particularly skeptical of products promising rapid or complete tinnitus elimination, as these claims contradict the current understanding of tinnitus mechanisms and available evidence on treatment outcomes.
Red Flags That Require Medical Attention
While many forms of tinnitus can be safely self-managed with OTC approaches, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical evaluation rather than self-treatment. Pulsatile tinnitus (sounds that beat in rhythm with your pulse) may indicate vascular abnormalities requiring medical intervention. Similarly, sudden-onset tinnitus, especially when accompanied by sudden hearing loss, requires urgent medical care as immediate treatment may prevent permanent damage.
Other warning signs include tinnitus accompanied by significant dizziness or vertigo, severe pain, discharge from the ear, or rapidly worsening symptoms. These combinations often indicate underlying conditions like Ménière’s disease, infections, or acoustic neuromas that require professional diagnosis and treatment. Unilateral tinnitus (affecting only one ear) should also prompt professional evaluation, particularly when accompanied by asymmetric hearing loss.
If you’re experiencing significant psychological distress, including anxiety, depression, or sleep disturbances due to your tinnitus, seeking professional help is essential regardless of the tinnitus characteristics. The psychological impact of tinnitus often responds well to specific therapeutic approaches like cognitive behavioral therapy, which can dramatically improve quality of life even when the tinnitus itself remains unchanged.
Creating Your Personal Relief Plan
The most successful tinnitus management approaches typically combine multiple strategies tailored to individual needs and lifestyle factors. Start by identifying your most troublesome tinnitus situations – perhaps nighttime when trying to sleep, quiet environments, or stressful periods – and target these specific scenarios first. Document your tinnitus patterns using smartphone apps or simple journals to identify triggers and track treatment responses objectively.
A comprehensive approach might include sound therapy devices for masking, targeted supplements based on identified deficiencies, stress management techniques, and environmental modifications to reduce tinnitus awareness. Begin with one intervention at a time, maintaining each for at least 3-4 weeks before judging effectiveness, as many approaches require consistent use before benefits emerge. Add additional strategies systematically, evaluating how they complement existing methods. For more insights, explore tinnitus treatment medication options that work.
Remember that tinnitus management is typically an ongoing process rather than a one-time solution. Be prepared to adjust your approach as needed based on changing symptoms, new research, or lifestyle changes. Many successful tinnitus managers report that their relief strategies evolve over time as they discover which combinations work best for their specific situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Navigating the complex world of tinnitus management often raises numerous questions about treatment approaches, timeframes, safety considerations, and practical matters. These frequently asked questions address common concerns related to over-the-counter tinnitus treatments based on current understanding and evidence. Remember that individual experiences vary considerably, and consulting healthcare providers about specific situations remains the most reliable approach.
As research continues to evolve, staying informed about emerging treatment options and updated recommendations is valuable for optimizing your tinnitus management strategy. Many professional organizations like the American Tinnitus Association provide regularly updated resources that complement the information provided here.
How long does it take for OTC tinnitus treatments to work?
Timeframes for experiencing benefits from OTC tinnitus treatments vary significantly depending on the approach. Sound therapy typically provides immediate relief during active use, though this effect initially disappears when the masking sound stops. With consistent use over 1-2 months, some users report residual inhibition where relief continues briefly after sound therapy ends, and gradual habituation to tinnitus may develop over 3-6 months of regular use.
Supplement approaches generally require more patience, with most requiring at least 4-12 weeks of consistent use before benefits might appear. Ginkgo biloba, for instance, typically shows any potential effects after 4-6 weeks minimum, while nutritional supplements addressing deficiencies may require 2-3 months to fully restore optimal levels. Earwax removal products offer the fastest potential resolution for appropriate cases, sometimes providing complete relief within days once impaction is successfully addressed.
Can multiple OTC treatments be used together safely?
Combining different types of OTC tinnitus treatments is generally safe and often more effective than single approaches, provided you follow certain guidelines. Sound therapy devices can safely complement most other interventions without significant interaction risks. Similarly, earwax management can be used alongside other approaches when appropriate for your situation.
Greater caution is needed when combining multiple supplements or medications. Herbal supplements may interact with each other or with medications, particularly those affecting blood clotting, blood pressure, or liver function. Before combining supplements, consult with a healthcare provider or pharmacist knowledgeable about supplement interactions. Start with lower doses of each when combining treatments and increase gradually while monitoring for side effects or unexpected interactions.
Are OTC tinnitus treatments covered by insurance or HSA/FSA?
Insurance coverage for OTC tinnitus treatments varies considerably depending on your specific plan and the type of intervention. Traditional health insurance typically doesn’t cover non-prescription supplements or basic sound machines purchased without a prescription. However, some plans cover specialized tinnitus masking devices when prescribed by an audiologist or physician as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) often provide more flexibility. Many sound therapy devices qualify as FSA/HSA-eligible expenses when used primarily for tinnitus management. Similarly, certain supplements may qualify when accompanied by a Letter of Medical Necessity from your healthcare provider documenting their use for a specific medical condition. Save all receipts and documentation of medical necessity for potential reimbursement or tax purposes.
What’s the difference between tinnitus maskers and hearing aids?
Tinnitus maskers and hearing aids serve different primary functions, though there is increasing overlap in modern devices. Traditional tinnitus maskers focus solely on generating sounds that blend with or cover tinnitus, without necessarily amplifying environmental sounds. They’re designed specifically for tinnitus relief rather than addressing hearing loss, though the masking effect can be achieved through various device types including earbuds, bedside machines, or wearable generators.
Hearing aids, conversely, primarily amplify environmental sounds to compensate for hearing loss, though many modern models include built-in tinnitus masking features as secondary functions. These combination devices can address both issues simultaneously, which is particularly valuable since hearing loss and tinnitus frequently co-occur. For those with both conditions, combination devices typically provide superior benefits compared to tinnitus-only solutions.
Can children with tinnitus use the same OTC treatments as adults?
Children with tinnitus require special considerations when exploring OTC treatment options. Sound therapy approaches are generally safe for children when used at appropriate volume levels and with proper supervision, particularly for school-aged children and adolescents. Simple white noise machines for sleep or background sound generators for studying environments can provide similar benefits to those experienced by adults. For more information on causes and relief options, you can explore tinnitus from ear infection and its management.
Supplement approaches require much greater caution in pediatric populations. Dosages, safety profiles, and effectiveness may differ significantly between children and adults. Most supplement studies focus exclusively on adult populations, leaving limited evidence for pediatric use. Always consult with a pediatric healthcare provider before initiating any supplement regimen for a child with tinnitus, regardless of the supplement’s safety profile in adults.
For any child experiencing tinnitus, professional evaluation should precede self-management approaches. Children may have difficulty accurately describing tinnitus symptoms, potentially masking serious underlying conditions that require medical intervention. Working with pediatric audiology specialists helps ensure appropriate diagnosis and age-appropriate management strategies.