Article-At-A-Glance
- White noise, breathing exercises, and finger-tapping techniques can provide immediate relief from tinnitus symptoms in as little as 30 seconds to 2 minutes
- Household items like fans and humidifiers can effectively mask tinnitus sounds without purchasing specialized equipment
- Simple physical techniques including targeted pressure points and jaw relaxation can quickly reduce the perception of ringing in the ears
- Certain foods and supplements like zinc, magnesium, and vitamin B12 may provide relief from tinnitus within hours
- Understanding when to seek medical attention for tinnitus is crucial, as persistent ringing can sometimes indicate underlying health conditions
That relentless ringing in your ears can feel like torture when you just need a moment of peace. Whether it just started or has been bothering you for years, there are immediate steps you can take right now to reduce that annoying sound. As someone who’s researched and worked with natural remedies extensively, I’ve gathered the most effective techniques that provide fast relief without medication.
Tinnitus—that persistent ringing, buzzing, or whooshing sound that only you can hear—affects nearly 50 million Americans. While there’s no instant cure, many natural methods can significantly reduce the volume and your awareness of the sound within minutes. These practical techniques have helped countless tinnitus sufferers find immediate relief when the noise becomes overwhelming.
Your environment, diet, stress levels, and even how you hold your jaw all impact tinnitus intensity. The good news is that these factors are within your control. Natural Sound Therapy has pioneered research into immediate tinnitus relief techniques that anyone can use at home without special equipment or medical intervention. Their approach combines ancient wisdom with modern science to tackle tinnitus at its source.
7 Fast-Acting Home Remedies to Quiet Tinnitus Now
“Tinnitus (Ringing in the Ears …” from www.youtube.com and used with no modifications.
When tinnitus strikes and you need relief fast, these seven techniques can help quiet the noise in as little as 30 seconds. Each method targets different potential causes of tinnitus, from muscle tension to circulation problems. For instance, some people have found CBD oil to be effective in managing their symptoms. Try them in sequence until you find what works best for your specific symptoms.
1. The 30-Second White Noise Trick
White noise works by providing your brain with a consistent, neutral sound that helps mask the tinnitus. Your auditory system can then shift focus away from the ringing, often providing immediate relief. Simply turn on a fan, air conditioner, or download a white noise app on your phone. Place the source near your bed or work area and let the gentle, consistent sound wash over you for at least 30 seconds. Many people report their tinnitus becoming significantly less noticeable within moments as their brain latches onto the external sound instead.
2. Quick Breathing Exercise to Calm Ringing
Stress amplifies tinnitus by increasing blood pressure and tension throughout your body, including the tiny muscles in your inner ear. This simple breathing technique can help break the stress-tinnitus cycle in under a minute.
- Sit comfortably and close your eyes
- Inhale deeply through your nose for 4 seconds
- Hold your breath for 7 seconds
- Exhale slowly through your mouth for 8 seconds
- Repeat 3-5 times, focusing entirely on your breath
This 4-7-8 breathing technique activates your parasympathetic nervous system (the “rest and digest” response), which reduces blood pressure and relaxes muscles that might be contributing to your tinnitus. Many people notice immediate improvement as blood flow normalizes throughout the head and neck region.
3. The Finger-Tapping Technique
This unusual but effective technique exploits a neurological trick to temporarily reduce tinnitus perception. Place your palms over your ears with fingers resting on the back of your head. Your index fingers should be on top of your middle fingers. Snap your index fingers off your middle fingers so they hit the base of your skull. Repeat this tapping 15-20 times. The vibration creates a brief masking effect that can interrupt the tinnitus pattern in your brain. Many users report up to several minutes of relief following this quick technique, making it perfect for sudden tinnitus spikes. For those interested in exploring other methods, consider learning about acupuncture for tinnitus as an alternative approach.
4. Salt Reduction for Same-Day Relief
Excess sodium affects fluid regulation in your body, including the sensitive fluid chambers of your inner ear. When these fluids become imbalanced, tinnitus often worsens. Cutting salt intake for even a single day can produce noticeable results for many sufferers. Replace high-sodium foods with fresh fruits and vegetables, and drink plenty of water to help flush excess sodium from your system. Pay special attention to hidden salt in processed foods, canned soups, and restaurant meals. Some tinnitus sufferers report improvement within hours of reducing sodium intake, especially if fluid retention was contributing to their symptoms.
How Music Helps Distract Your Brain From the Ringing
Music therapy offers immediate relief for many tinnitus sufferers by giving your brain something more complex and pleasant to focus on. Unlike white noise, music engages multiple areas of your brain simultaneously, creating a powerful distraction from the ringing. Choose music with a variety of frequencies—classical pieces with both high and low tones work particularly well. Instrumental music tends to be more effective than songs with lyrics, as your brain can focus on the pure sound rather than processing words.
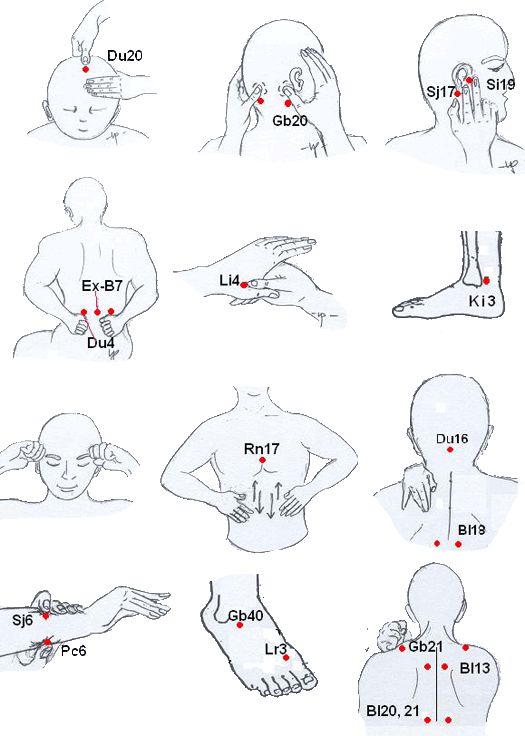
Pressure Point Techniques to Try When Ringing Won’t Stop
“Home – Hearing Tinnitus” from www.pinterest.com and used with no modifications.
Traditional medicine has identified several pressure points that can provide rapid tinnitus relief by improving circulation and releasing tension in areas connected to your ears. These techniques have been used for thousands of years and require nothing but your hands and a few minutes of quiet focus. For more detailed advice, consider these tips to manage tinnitus effectively.
When applying pressure to these points, use your thumb or index finger to press firmly but gently. The sensation should be strong but not painful. Hold each point for 30-60 seconds while taking slow, deep breaths. You may feel a subtle pulsing under your fingertip—this is normal and indicates improved blood flow to the area.
For best results, try these pressure points when you’re in a relaxed position, either sitting or lying down. Many people find these techniques most effective when done in a quiet room with minimal distractions, allowing you to focus on the sensations and any changes in your tinnitus.
Behind-the-Ear Pressure Points
The hollow area directly behind your earlobe where your jaw meets your skull contains a pressure point that can significantly reduce tinnitus intensity. Using your index fingers, locate the soft depression behind each ear and apply firm, circular pressure for 30 seconds. This point connects to nerve pathways that influence both hearing and relaxation. Many tinnitus sufferers report an immediate “opening” sensation in their ears, followed by a noticeable reduction in ringing. This technique works particularly well for tinnitus caused by stress or muscle tension.
Hand Reflexology for Ear Health
Your hands contain reflex points that correspond to your ears and can provide fast tinnitus relief. The most effective point is located in the center of the palm of each hand. Press your thumb firmly into this area and massage in small circles for 1-2 minutes per hand. You may feel tenderness—this actually indicates the point is working to rebalance the energy flow to your ears.
Another powerful reflex point is located on the uppermost segment of your ring finger, just below the fingernail. Gently squeeze this area between your opposite thumb and index finger for 30 seconds on each hand. This particular point has been shown to influence the auditory system directly, with many people reporting a temporary decrease in tinnitus volume within minutes of stimulation.
Quick Physical Movements That Reduce Tinnitus
“exercises to eliminate tinnitus …” from claso.net and used with no modifications.
Physical tension, especially in your neck, shoulders, and jaw, can dramatically increase tinnitus symptoms. These areas share nerve connections with your auditory system, creating a direct pathway for tension to amplify the ringing in your ears. The following movements release this tension and can provide immediate relief. For maximum benefit, perform these exercises in a quiet room where you can fully focus on the sensations in your body and any changes in your tinnitus symptoms.
Neck Stretches That Ease Ear Pressure
Tight neck muscles can compress blood vessels and nerves that connect to your ears, intensifying tinnitus symptoms. A simple neck release can provide immediate relief. Sit comfortably and slowly tilt your head toward your right shoulder until you feel a gentle stretch along the left side of your neck. Hold for 30 seconds, breathing deeply, then repeat on the opposite side. Next, gently roll your head in a half-circle from one shoulder to the other (avoid rolling backward). Repeat 5 times in each direction.
For deeper relief, try the scalene stretch. Place your right hand on your left collarbone, then tilt your head back and toward the right. This stretches the scalene muscles, which often refer tension to the ears. Hold for 20 seconds, then switch sides. Many tinnitus sufferers report immediate improvement after performing these stretches, particularly if their symptoms worsen when looking down or after long periods at a desk.
Jaw Exercises for TMJ-Related Tinnitus
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction is a common but often overlooked cause of tinnitus. The jaw joint sits directly in front of your ear canal, and tension here can directly impact your perception of ringing. To release this tension, place your fingertips on your jaw joint (just in front of your ears) and open your mouth slowly while applying gentle pressure. Open and close 10 times, then move your jaw side to side 10 times.
For deeper relief, try the jaw resistance technique. Place your fist under your chin and apply gentle upward pressure as you try to open your mouth. Hold for 5 seconds, then relax. Repeat 5 times. This resistance training helps recalibrate the muscles that may be pulling your jaw out of alignment and contributing to your tinnitus. Many people with TMJ-related tinnitus report significant improvement within minutes of performing these exercises.
The Head Tap Method
This unusual but effective technique creates a temporary masking effect that can interrupt tinnitus patterns. Place your palms flat against your ears with your fingers wrapped around the back of your head. Your index fingers should rest on top of your middle fingers. Snap your index fingers off your middle fingers onto the base of your skull, creating a drumming sound. Repeat this tapping 15-20 times. The vibration temporarily disrupts the nerve signals causing your tinnitus, providing a brief but welcome respite from the noise. Some people report relief lasting several minutes to an hour after performing this simple technique. For more insights, check out this expert Q&A on tinnitus management.
Emergency Supplements and Foods That Help Within Hours
“A Comprehensive Review on …” from www.mdpi.com and used with no modifications.
Certain nutritional deficiencies can trigger or worsen tinnitus, and addressing these gaps can sometimes provide same-day relief. While supplements work best as part of a long-term strategy, many tinnitus sufferers report noticeable improvement within hours of taking specific nutrients. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen, especially if you take medications that might interact with these nutrients.
Zinc-Rich Foods That Combat Ringing
Zinc deficiency has been directly linked to tinnitus in multiple studies, and supplementing this mineral can provide rapid relief for some sufferers. The best food sources include oysters (the richest natural source), grass-fed beef, pumpkin seeds, and lentils. For fast absorption, try a sublingual zinc supplement (placed under the tongue), which enters your bloodstream directly rather than going through your digestive system. Many people report a noticeable reduction in tinnitus intensity within 2-3 hours of addressing zinc deficiency, particularly if their symptoms fluctuate with stress or illness.
Vitamin B12 Sources for Fast Relief
B12 deficiency affects the myelin sheath that protects nerve cells, including those involved in hearing. Low B12 levels can cause tinnitus that responds quickly to supplementation. For immediate intake, consider B12-rich foods like clams, beef liver, nutritional yeast, or fortified cereals. Sublingual B12 supplements can provide even faster absorption, with many users reporting improved symptoms within hours. This vitamin is particularly effective for tinnitus that’s accompanied by fatigue, brain fog, or numbness and tingling in the extremities—all common signs of B12 deficiency.
Magnesium’s Role in Quieting Tinnitus
Magnesium regulates nerve signals throughout your body, including those in your auditory system. Low magnesium levels can cause nerve cells to become hyperactive, potentially intensifying tinnitus. For quick intake, reach for magnesium-rich foods like dark chocolate (70%+ cacao), avocados, bananas, and leafy greens. Magnesium glycinate or threonate supplements are well-absorbed forms that may provide faster relief than food sources alone. Many tinnitus sufferers report reduced ring intensity within 1-2 hours of taking magnesium, with the effect becoming stronger over several days of consistent supplementation. For those exploring other options, you might consider reading about Tinaway vs Quietus supplements for tinnitus relief.
For enhanced absorption, pair magnesium with vitamin B6 (found in chickpeas, tuna, and potatoes), which helps transport the mineral into cells where it’s needed most. This combination can be particularly effective for tinnitus that worsens during periods of stress, as both nutrients help regulate your body’s stress response.
Pineapple: Nature’s Anti-Inflammatory for Ears
Pineapple contains bromelain, a powerful enzyme with natural anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce swelling in the ear canal and cochlea. This tropical fruit works quickly to reduce inflammation throughout your body, including the delicate structures of your inner ear. Just one cup of fresh pineapple provides a therapeutic dose of bromelain that can begin working within 30-60 minutes of consumption.
For maximum effectiveness, eat pineapple on an empty stomach or between meals. This allows the bromelain to be absorbed more quickly into your bloodstream. If fresh pineapple isn’t available, look for natural pineapple juice without added sugar, though the bromelain content will be somewhat lower. Many tinnitus sufferers report that incorporating pineapple into their daily diet not only provides immediate relief but also helps prevent severe tinnitus episodes when consumed regularly.
When to See a Doctor About Your Tinnitus
“Understanding and Managing Tinnitus: My …” from hearingaiddoctors.com and used with no modifications.
While these natural remedies can provide significant relief for many people, certain tinnitus symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. Tinnitus can sometimes be a warning sign of more serious conditions that require professional treatment. If your tinnitus developed suddenly, is accompanied by hearing loss, dizziness, or occurs only in one ear, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider promptly rather than relying solely on home remedies.
Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical care if your tinnitus is accompanied by any of these red flags: sudden hearing loss, severe dizziness or vertigo, tinnitus that pulses in rhythm with your heartbeat, or ringing that occurs exclusively in one ear. These symptoms could indicate potentially serious conditions like Ménière’s disease, acoustic neuroma, or vascular problems that require professional evaluation. For more insights, check out this expert audiologist’s answers to common tinnitus questions.
Additionally, if you experience severe headache along with your tinnitus, especially if it’s the worst headache of your life, this could signal a neurological emergency requiring immediate medical attention. Tinnitus that develops after a head injury should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional, as it may indicate traumatic damage to the auditory system or brain that needs specialized treatment. For more information on managing tinnitus, you can refer to Harvard Health Publishing.
What to Tell Your Doctor About Your Symptoms
When consulting a healthcare provider about tinnitus, come prepared with specific details that will help them make an accurate diagnosis. Track when your tinnitus started, what it sounds like (ringing, buzzing, clicking, pulsing), whether it’s constant or intermittent, and if certain activities or times of day make it better or worse. Note any medications you’re taking, recent illnesses, changes in hearing, or exposure to loud noises.
Be sure to mention any home remedies you’ve tried and whether they provided relief. This information helps your doctor determine potential causes and create an effective treatment plan. Don’t hesitate to ask about specialized treatments like tinnitus retraining therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, or whether you might benefit from a referral to an ENT specialist or audiologist who specializes in tinnitus management.
Your Action Plan for Long-Term Tinnitus Management
“tinnitus retraining therapy” from www.frontiersin.org and used with no modifications.
While the immediate relief techniques covered in this article can help during tinnitus flare-ups, developing a comprehensive management strategy will provide more consistent relief over time. Start by identifying your personal tinnitus triggers—common ones include stress, certain foods, loud environments, and lack of sleep. Once you know what worsens your symptoms, you can take proactive steps to minimize exposure.
Create a tinnitus toolkit containing items that provide quick relief during flare-ups. This might include earbuds with your favorite masking sounds pre-loaded, stress-relief techniques you can do anywhere, and portable healthy snacks that support ear health. Having these resources readily available prevents panic when tinnitus suddenly intensifies and gives you a sense of control over your symptoms.
Consider keeping a tinnitus journal to track patterns in your symptoms. Note the time of day, your stress level, recent foods, activities, and the effectiveness of different relief strategies. Over time, this journal will reveal valuable insights about your unique tinnitus profile and help you refine your management approach for maximum relief. Remember that consistency is key—the techniques that work best for you should become part of your daily routine, not just emergency measures.
Frequently Asked Questions
As you work to manage your tinnitus, you’ll likely have questions about what helps, what hurts, and what to expect. The following answers address the most common concerns among tinnitus sufferers and provide science-backed information to guide your relief journey.
Can stress make tinnitus worse?
Yes, stress is one of the most significant tinnitus amplifiers. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones that can increase blood pressure, muscle tension, and nerve sensitivity—all of which can intensify tinnitus. The brain’s attention system also becomes more sensitive during stress, making you more aware of the ringing sound that might otherwise fade into the background. For insights on how stress management techniques like transcendental meditation can help alleviate symptoms, check out this article.
This creates a vicious cycle: tinnitus causes stress, which makes tinnitus more noticeable, leading to more stress. Breaking this cycle through stress management techniques like meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, or gentle exercise can significantly reduce tinnitus perception, often within minutes of completing the activity. For more insights, you can explore acupuncture for tinnitus and its potential benefits.
Is tinnitus permanent or will it go away on its own?
Tinnitus duration varies greatly depending on its cause. Temporary tinnitus, often resulting from exposure to loud noise, ear infections, or certain medications, typically resolves within hours to weeks once the underlying cause is addressed. However, tinnitus related to permanent hearing damage, age-related hearing loss, or certain health conditions may be long-term. Even persistent tinnitus can become less bothersome over time as your brain naturally adapts through a process called habituation, where the brain gradually filters out the unwanted sound from conscious awareness.
Does caffeine affect tinnitus symptoms?
Caffeine’s Effect on Tinnitus: What Research Shows
While some studies suggest that caffeine might exacerbate tinnitus symptoms, others show no significant effect. It’s important to consider individual variations and consult with experts. For more insights, you might find it helpful to ask the expert for common tinnitus questions.
The relationship between caffeine and tinnitus is complex and highly individual. While some studies suggest caffeine may worsen symptoms due to its effects on blood pressure and stimulation of the nervous system, other research indicates that sudden caffeine withdrawal can actually trigger or worsen tinnitus in regular consumers.
A 2014 study published in the American Journal of Medicine found that women who consumed higher amounts of caffeine (approximately 450-600mg daily) actually reported lower incidences of tinnitus than those who consumed less.
The most effective approach is to track your personal response to caffeine. Try reducing your intake gradually over a week (sudden elimination can cause withdrawal symptoms that worsen tinnitus) and note any changes in your symptoms. Pay attention to not just coffee but also tea, chocolate, energy drinks, and certain medications that contain caffeine.
If you find caffeine triggers your tinnitus, consider switching to alternatives like chicory root coffee, herbal teas, or golden milk (made with turmeric and warm plant-based milk). These can provide a satisfying ritual without the potential tinnitus-aggravating effects of caffeine.
For those who don’t notice negative effects from caffeine, there’s likely no need to eliminate it completely. However, monitoring your consumption and avoiding caffeine in the late afternoon and evening can improve sleep quality, which often helps reduce tinnitus intensity.
Are there any foods I should avoid if I have tinnitus?
Several food categories have been linked to tinnitus flare-ups in sensitive individuals. High-sodium foods can alter fluid balance in the inner ear, potentially increasing pressure and worsening symptoms. Processed foods containing MSG or artificial sweeteners trigger tinnitus in some people by affecting neurotransmitter activity. Alcohol and quinine (found in tonic water) can temporarily affect blood flow to the ear and intensify ringing. The best approach is elimination testing—remove suspected trigger foods for two weeks, then reintroduce them one at a time while monitoring your symptoms closely. For more insights, you might want to explore Lipo-Flavonoid Plus and its effects on tinnitus.
Can hearing aids help with tinnitus relief?
Modern hearing aids can provide significant tinnitus relief through multiple mechanisms. By amplifying environmental sounds, they help mask the internal ringing and redirect your attention to external sounds. Many current models include built-in sound therapy features that generate customized sounds designed specifically to counteract your particular tinnitus frequency.
Hearing aids are particularly effective for people whose tinnitus is associated with hearing loss. By restoring auditory stimulation to the brain, they can help “retrain” auditory pathways that may be generating the phantom sounds. Some users report immediate improvement when wearing their devices, while others experience gradual reduction in tinnitus awareness over several weeks of consistent use. For those interested in alternative options, exploring the Lenire device might provide additional insights into tinnitus management.
For best results, look for an audiologist who specializes in tinnitus management and can program your hearing aids specifically for tinnitus relief rather than just hearing enhancement. Many offer trial periods that allow you to test different models and features before making a financial commitment.
If you’re hesitant about traditional hearing aids, consider newer, more discreet options like completely-in-canal devices or even over-the-counter sound amplifiers as a starting point. The key is to increase auditory stimulation to counteract your brain’s tendency to “fill in” missing frequencies with tinnitus sounds. For more tips, you can check out tips to manage tinnitus.